Turtling Syndrome: Identifying Symptoms and Effective Solutions
Turtling syndrome is a condition where the penis retracts into the body, and it can affect men of various ages. This phenomenon often causes distress and confusion, but understanding its origins and treatments can help manage the condition effectively. Turtling syndrome often occurs after surgery or due to temperature changes, obesity, or certain medical conditions.
This condition may come with various symptoms, such as discomfort, frequent urination, and issues with sexual health. Identifying these symptoms early is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Effective management of turtling syndrome involves understanding both surgical and non-surgical treatments available, which can vary depending on individual circumstances.
Proper diagnosis and management of turtling syndrome can significantly improve quality of life. Knowing what to expect and exploring all potential treatments can provide relief and better outcomes for those affected.
Key Takeaways
- Turtling syndrome involves retraction of the penis into the body.
- Symptoms include discomfort and issues with sexual health.
- Various treatments are available, tailored to individual needs.
Understanding Turtling Syndrome
Turtling Syndrome involves complex issues related to both congenital and acquired conditions affecting male genital anatomy. This can influence one’s physical health and quality of life.
Definition and Classification
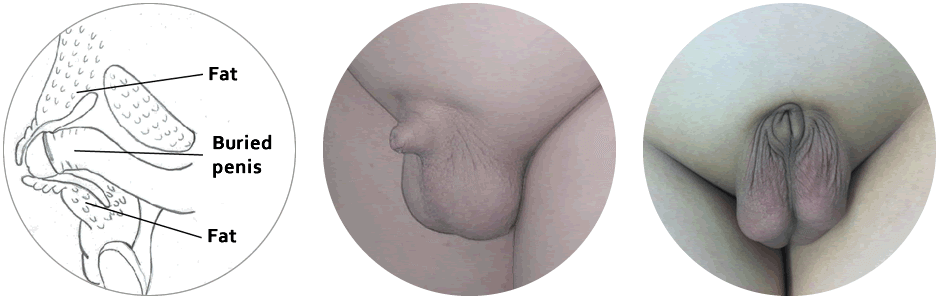
Turtling Syndrome is often referred to using terms like “Buried Penis” or “Hidden Penis”. This condition describes a situation where the penis is hidden below the surface of the pubic skin.
There are two main types: congenital and acquired. Congenital cases are present from birth, while acquired cases develop later in life. Within acquired cases, Adult Acquired Buried Penis (AABP) is particularly important. The classification system for this condition helps doctors categorize severity and decide on treatment.
Congenital vs Acquired
Congenital Turtling Syndrome presents at birth. It may be related to developmental issues during fetal growth. Some children have additional genitourinary anomalies.
Acquired Turtling Syndrome happens due to factors like obesity, trauma, or chronic inflammation. Adult Acquired Buried Penis (AABP) commonly appears in men due to significant weight gain, scarring, or post-surgical complications. Understanding whether a case is congenital or acquired is essential for deciding on the right approach for treatment.
Anatomical Considerations
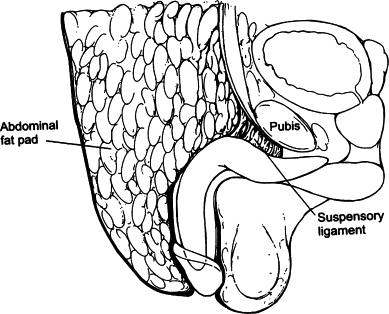
Key anatomical issues in Turtling Syndrome include improper attachment of the penile skin, abnormal fat distribution, and scarring. These factors either conceal or alter the visual and functional appearance of the penis.
In children, congenital issues might be mainly skin-related. In adults, especially with AABP, obesity-related fat pads or scar tissue from surgeries are significant causes. Proper anatomical examination is crucial for identifying the corrective measures needed for treatment. Surgical intervention, weight loss, or skin grafts may be considered based on these findings.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and proper diagnostic procedures is critical for managing turtling syndrome. This section covers the physical symptoms, psychological impact, and the steps for accurate diagnosis.
Physical Symptoms
Turtling syndrome presents with several noticeable physical symptoms. Most commonly, you might experience swelling and discomfort in the genital area. Another key symptom is the retraction of the penis into the pubic region, often exacerbated by certain physical activities or cold temperatures.
Patients may report pain during urination or physical activity. It’s important to document the frequency and severity of these symptoms. Keeping track of any patterns can help your healthcare provider better understand your condition.
When observing these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice. Delaying a visit to the doctor can make symptoms worse and lead to complications.
Psychological Impact
Dealing with turtling syndrome can have significant psychological impacts. Individuals often suffer from low self-esteem due to the physical symptoms. This can affect your mental health, leading to depression and anxiety.
Social situations may become stressful, and you may feel embarrassed or isolated. The need for frequent medical appointments can add to your stress. It is crucial to seek mental health support alongside physical treatment.
Open communication with friends, family, and healthcare providers can help alleviate some of the psychological burden. Remember, addressing your mental health is as important as managing your physical symptoms.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing turtling syndrome involves a combination of physical exams and imaging tests. Initially, your doctor will perform a thorough physical examination to observe the retraction and identify any associated swelling or discomfort.
In some cases, a retrograde urethrogram might be used. This test involves X-raying the bladder and urethra to find any structural abnormalities. Blood tests may also be conducted to rule out other underlying conditions.
It is crucial to follow your doctor’s instructions for these tests to get an accurate diagnosis. This will help develop an effective treatment plan tailored to your needs. Regular follow-ups are necessary to monitor progress and make adjustments to your treatment.
Complications and Related Conditions
Complications associated with turtling syndrome can include infections, urinary and sexual dysfunction, and skin issues like lymphedema. Understanding these complications helps in managing the condition effectively.
Infections and Inflammation
Infections are a major concern with turtling syndrome. You may experience Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) due to difficulty in maintaining hygiene. The risk of Hidradenitis Suppurativa, an inflammation of sweat glands, increases with skin folds. This can cause painful abscesses and boils.
Lichen Sclerosus, a chronic skin condition, might occur, leading to white patches on the genital area. If left untreated, these infections could escalate to Penile Cancer. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of infections are crucial to avoid severe complications.
Urinary and Sexual Dysfunction
Turtling syndrome can impact urination and sexual function. Urinary difficulties, like frequent UTIs, arise from poor hygiene caused by skin folds. You may experience urinary retention or incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Sexual dysfunction is prevalent among affected individuals. Issues such as erectile dysfunction can occur, making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection. This can lead to psychological stress and affect relationships.
Treatments like skin grafting might be necessary to remove excess skin and improve both urination and sexual function. Split-Thickness Skin Grafts can provide relief and prevent further complications.
Lymphedema and Skin Issues
Lymphedema is a significant issue, where excess fluid builds up in the tissues causing swelling. Genital lymphedema and scrotal lymphedema can make walking or sitting uncomfortable.
Swelling can lead to secondary skin infections and other skin problems. Edema, or fluid retention, can stretch the skin and lead to Hidradenitis Suppurativa, causing painful, swollen lumps.
Your treatment might include compressive therapy and skin grafts to manage the swelling. In severe cases, surgical interventions like split-thickness skin grafts are performed to alleviate symptoms and improve mobility.
Surgical and Non-Surgical Treatments
Treating “turtling syndrome” (also known as buried penis) involves lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgery. Each treatment focuses on different aspects, including weight loss, medications, and various surgical procedures. Below, we’ll explore these aspects in detail.
Lifestyle Changes and Medication
Changing your lifestyle can greatly improve this condition. Weight loss is often critical. Obesity increases the risk of a buried penis. You should aim to eat a balanced diet and stay active.
Doctors might prescribe medications to aid in weight loss. Psychological counseling can help manage emotional challenges that come with these lifestyle changes.
Antibiotics may be necessary if there are any infections related to the buried penis condition. Skincare products might also help manage skin issues around the genital area.
Surgical Options
For severe cases, surgery might be required. Buried penis repair includes several procedures. Circumcision can help by removing excess foreskin.
Panniculectomy and abdominoplasty (tummy tuck) remove extra abdominal skin. Scrotoplasty and scrotectomy are surgeries on the scrotum to remove excess skin or tissue.
Escutcheonectomy removes excess skin and fat from the lower abdomen. Skin grafting may be necessary for extensive repairs. Suction lipectomy helps remove fat deposits surgically.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
After surgery, proper care is important. Your doctor will give you specific instructions. Antibiotics help prevent infections after the surgery. Regular check-ups ensure that healing is progressing well.
Wound care is crucial, and you must follow the doctor’s guidelines closely. This might include cleaning the area and applying prescribed ointments.
Psychological counseling can help as you adapt to changes after surgery. Emotional support is key for a smooth recovery.
Considerations for Specific Populations
Turtling syndrome affects different populations in unique ways. It’s important to tailor care and management strategies to the specific needs of each group, including children, adolescents, the elderly, and the morbidly obese.
Children and Adolescents
For children and adolescents, early detection and treatment are essential. This age group may experience significant psychological impacts due to the condition’s effect on appearance and social interactions. You should focus on maintaining hygiene and sexual function to prevent complications arising from poor hygiene practices.
Regular medical check-ups are important. Growth and development must be monitored to ensure that turtling syndrome does not interfere with normal progression. Surgical and non-surgical treatments might be considered depending on the severity. Supportive counseling can help young patients cope with the social and emotional aspects of the syndrome.
The Elderly and Morbidly Obese
In the elderly and morbidly obese populations, turtling syndrome presents additional challenges. Poor hygiene due to limited mobility or morbid obesity can increase the risk of infections. You should pay particular attention to maintaining cleanliness and monitoring for any signs of infection.
For the morbidly obese, managing weight is crucial. Weight loss can potentially reduce the severity of symptoms. In the elderly, ensure regular follow-ups to address any emerging complications promptly. Both groups may benefit from personalized physical therapy to improve overall function and prevent further decline in health. Ensure that any treatment plan is adaptable to their specific physical limitations.
Outcomes and Prognosis
Understanding the outcomes and prognosis of turtling syndrome involves considering the potential improvements in quality of life, the associated risks and success rates, and the requirements for long-term management.
Quality of Life Improvements
Addressing turtling syndrome can lead to significant quality of life improvements. Many patients report enhanced self-esteem and better mental health after treatment, mainly because the condition is medically and emotionally challenging. Reducing visible scar tissue and improving genital appearance can decrease depression levels and enhance sexual function.
Moreover, you may find that physical symptoms like discomfort and restricted movement improve significantly after treatment. Patients often report better satisfaction with their overall physical exam results, noting marked improvements in their erection capabilities and daily function.
Risks and Success Rates
Treatments for turtling syndrome come with various risks and success rates. Surgery, for example, can lead to complications such as infection, excessive bleeding, or issues with cicatrix formation. However, many patients experience a high success rate, with significant improvements in both ligaments and genital appearance.
Non-surgical options, although less invasive, typically have lower success rates but also pose fewer risks. It’s essential to discuss these options with your doctor to understand which treatment aligns best with your needs and medical history.
Long-Term Management
Long-term management of turtling syndrome involves regular physical exams and consistent follow-ups to monitor any changes or recurrences. You may need ongoing therapy to maintain the results, particularly regarding ligaments and scar tissue.
Additionally, managing lifestyle factors, such as maintaining a healthy weight and practicing regular exercise, can contribute to sustained improvements. Psychological counseling may be recommended to continue addressing any lingering mental health issues, improving your self-esteem and reducing the risk of depression.
Regular consultations with healthcare professionals ensure that any new complications are promptly addressed, and treatments can be adjusted to maintain the quality of life improvements achieved through initial treatment efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding the indications, treatments, and contributing factors of turtling syndrome is important. The following questions address key aspects of this condition.
What are the early signs of a retracted male organ?
Early signs may include a noticeable reduction in size and an inability to maintain normal length. It might also feel colder than normal due to reduced blood flow.
Which symptoms are indicative of the condition related to a well-retracted male organ?
Symptoms can include difficulty during urination, discomfort, and possible infection due to trapped moisture. The skin may also appear wrinkled or puckered.
What treatments are available for correcting the appearance of a retracted male organ?
Treatments include topical creams to keep the area moisturized and warm compresses to improve blood flow. In some cases, doctors may recommend minor surgical procedures to correct persistent issues.
How does this condition typically present in infants?
In infants, it often appears as a smaller-than-expected organ, sometimes retracting almost entirely into the body. It can be normal and usually requires simple hygiene and monitoring.
What factors may contribute to the appearance of a smaller male organ size?
Factors include cold temperatures, anxiety, and excess body fat. Underlying medical conditions, such as Peyronie’s disease, can also contribute.
Can adults develop the condition associated with excessive retraction of the male organ, and what are its manifestations?
Adults can develop this condition, especially due to aging or health issues like diabetes. Manifestations include a more retracted appearance and potential complications with urination and discomfort during physical activities.
Adults can develop this condition, especially due to aging or health issues like diabetes. Manifestations include a more retracted appearance and potential complications with urination and discomfort during physical activities.