Vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining good eyesight. A balanced diet with the right vitamins can help prevent eye problems and maintain good vision. The most important vitamins for eye health include Vitamin A, C, E, and B complex, as well as carotenoids, Omega-3s, and minerals such as zinc and copper. Learn what vitamins improve eyesight.
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining good eyesight. It helps prevent night blindness and dry eyes, and it is also important for the health of the retina. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the eyes from free radicals and oxidative stress. Vitamin E is another antioxidant that helps protect the eyes from damage caused by UV rays and other environmental factors. B complex vitamins, such as riboflavin and niacin, are also important for maintaining good eye health.
Carotenoids are pigments that give fruits and vegetables their bright colors. They are also important for maintaining good eyesight. Lutein and zeaxanthin are two carotenoids that are particularly important for eye health. They help protect the eyes from damage caused by blue light and UV rays. Omega-3 fatty acids are also important for maintaining good eye health. They help prevent dry eyes and reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
Understanding Eye Health
Maintaining good eye health is important for overall well-being. The eyes are complex organs that are responsible for vision. They are made up of several components, including the cornea, retina, macula, optic nerve, and blood vessels. Each of these components plays a crucial role in ensuring that the eyes function properly.
One of the most important factors in maintaining good eye health is proper nutrition. Research has shown that certain vitamins and nutrients can help prevent or reduce the risk of eye diseases and conditions. These vitamins and nutrients include vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, B complex, riboflavin, niacin, carotenoids, omega-3s, thiamine, lutein, and zeaxanthin.
Vitamin A is essential for good vision and helps prevent night blindness. It is found in foods such as liver, sweet potatoes, carrots, and spinach. Vitamin C helps maintain healthy blood vessels in the eyes and is found in citrus fruits, broccoli, and strawberries. Vitamin E is an antioxidant that helps protect cells in the eyes from damage and is found in nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
B complex vitamins, including riboflavin and niacin, are important for overall eye health. Riboflavin helps prevent cataracts and is found in dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals. Niacin helps reduce the risk of glaucoma and is found in meat, fish, and whole grains.
Carotenoids, including lutein and zeaxanthin, are pigments that are found in the macula of the eye. They help protect the eyes from harmful blue light and reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts. They are found in leafy green vegetables, eggs, and yellow and orange fruits and vegetables.
Omega-3 fatty acids are important for maintaining healthy blood vessels in the eyes and reducing the risk of macular degeneration. They are found in fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna, as well as flaxseed and walnuts. Thiamine is important for nerve function in the eyes and is found in whole grains, lean meats, and fortified cereals.
Overall, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help promote good eye health. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new vitamin or supplement regimen.
Role of Vitamins in Eye Health
Vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining good eye health. Several vitamins, including Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, and B Vitamins, have been linked to improved eyesight and a reduced risk of eye diseases.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining good vision. It helps maintain a clear cornea, which is the outside covering of the eye, and is also a component of rhodopsin, a protein in the eye that helps you see in low light conditions. A deficiency in Vitamin A can lead to night blindness and other eye problems.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps protect the eye from damage caused by free radicals. It also helps the body absorb iron, which is important for eye health. Studies have shown that people who consume more Vitamin C have a lower risk of developing cataracts and age-related macular degeneration.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is another antioxidant that helps protect the eye from damage caused by free radicals. It also helps reduce inflammation and may help prevent cataracts and age-related macular degeneration.
B Vitamins
B Vitamins, including B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are important for maintaining good eye health. They help reduce levels of homocysteine, an amino acid that can damage blood vessels in the eye and increase the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
Beta-Carotene
Beta-carotene is a type of Vitamin A that is found in many fruits and vegetables, including carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach. It is important for maintaining good vision and can help reduce the risk of cataracts and age-related macular degeneration.
Supplements
While it is best to get your vitamins from a healthy diet, some people may benefit from taking supplements. A multivitamin that contains a variety of vitamins and minerals, including those important for eye health, can be a good option for some people. However, it is important to talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
In conclusion, vitamins are essential for maintaining good eye health. Eating a healthy diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, and other nutrient-rich foods is the best way to ensure that you are getting all the vitamins and minerals your body needs. However, some people may benefit from taking supplements, and it is important to talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
Specific Vitamins and Their Benefits
When it comes to maintaining healthy eyesight, certain vitamins play a crucial role. In this section, we will explore the benefits of specific vitamins and how they can help prevent vision loss and other eye-related issues.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy vision. It helps prevent night blindness and is crucial for the proper functioning of the retina. Vitamin A also plays a role in maintaining a clear cornea, which is the outermost layer of the eye.
According to Healthline, Vitamin A is also a component of rhodopsin, a protein in the eye that helps you see in low-light conditions. A deficiency in Vitamin A can result in vision loss, particularly in older adults.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an antioxidant that can help prevent age-related eye diseases. According to Medical News Today, studies have shown that Vitamin C can help reduce the risk of cataracts and slow the progression of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is another antioxidant that can help prevent eye diseases. It can help protect the eyes from damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells. According to Forbes, Vitamin E has been shown to reduce the risk of cataracts and slow the progression of AMD.
B Vitamins
B Vitamins, particularly B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are important for maintaining healthy eyes. According to Cleveland Clinic, these vitamins can help reduce the risk of AMD and prevent vision loss. They also play a role in the production of red blood cells, which are necessary for delivering oxygen to the eyes.
In conclusion, incorporating these specific vitamins into your diet can help maintain healthy eyesight and prevent vision loss. However, it’s important to note that taking high doses of these vitamins can be harmful, so it’s best to get them through a balanced diet or a multivitamin supplement.
Importance of Minerals for Eyesight
Minerals play a crucial role in maintaining healthy eyesight. Zinc and copper, in particular, are essential minerals that contribute to the overall health of the eyes.
Zinc is a mineral that is found in high concentrations in the retina and is necessary for the proper functioning of the visual system. It helps to protect the retina from damage caused by light exposure and oxidative stress. Zinc also plays a role in the production of melanin, a pigment that helps to protect the eyes from harmful UV rays.
Copper is another mineral that is important for maintaining healthy eyesight. It helps to prevent oxidative damage to the eyes and is involved in the production of collagen, a protein that is essential for maintaining the structure of the eye.
Both zinc and copper can be obtained from a healthy diet that includes foods such as seafood, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. However, some people may need to take supplements to ensure that they are getting enough of these minerals.
It is important to note that taking too much zinc can actually be harmful to the eyes. High levels of zinc can interfere with the absorption of other minerals, such as copper, and can lead to a deficiency. Therefore, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional before taking any zinc supplements.
In summary, minerals such as zinc and copper are important for maintaining healthy eyesight. While these minerals can be obtained from a healthy diet, some people may need to take supplements to ensure that they are getting enough. However, it is important to be mindful of the potential risks associated with taking too much of these minerals and to speak with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
Carotenoids and Eye Health
Carotenoids are a group of pigments that are naturally found in plants and are responsible for their vibrant colors. Some carotenoids, such as lutein, zeaxanthin, and beta-carotene, are particularly important for maintaining good eye health.
Lutein and zeaxanthin are two carotenoids that are found in high concentrations in the macula, a small area in the center of the retina that is responsible for sharp, detailed vision. These carotenoids act as antioxidants and help to protect the macula from damage caused by harmful blue light and free radicals. Studies have shown that higher levels of lutein and zeaxanthin in the diet are associated with a lower risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
Beta-carotene is another carotenoid that is converted into vitamin A in the body, which is essential for maintaining healthy vision. Vitamin A helps to protect the surface of the eye and is important for the functioning of the retina. However, it is important to note that taking high doses of beta-carotene supplements has been associated with an increased risk of lung cancer in smokers.
Leafy greens, such as kale, spinach, and Swiss chard, are excellent sources of lutein and zeaxanthin. Other good sources include yellow and orange fruits and vegetables, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, and mangoes. Beta-carotene is found in high amounts in orange and yellow fruits and vegetables, such as cantaloupe, apricots, and squash.
In summary, carotenoids, including lutein, zeaxanthin, and beta-carotene, are important for maintaining good eye health. Including a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in the diet can help to ensure that these important nutrients are consumed in adequate amounts.
Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that play a vital role in maintaining healthy eyesight. They are a type of polyunsaturated fat that cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through the diet. There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
DHA is the most abundant omega-3 fatty acid in the retina and is essential for the normal development and function of the eyes. It is a major component of the photoreceptor cells in the retina and is involved in the transmission of visual signals from the eye to the brain. Studies have shown that DHA can help prevent age-related vision loss and improve visual acuity in people with dry eye syndrome.
EPA is also important for eye health and has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the risk of developing age-related macular degeneration (AMD). AMD is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults and is caused by the deterioration of the macula, the central part of the retina that is responsible for sharp, detailed vision.
Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are rich sources of EPA and DHA. Flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts are good sources of ALA, which can be converted into EPA and DHA in the body. Omega-3 supplements are also available and can be a convenient way to increase your intake of these essential fatty acids.
It is important to note that while omega-3 fatty acids are beneficial for eye health, they should not be used as a substitute for regular eye exams and proper eye care. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods, along with regular exercise and good sleep habits, can help support overall eye health.
Age-Related Eye Conditions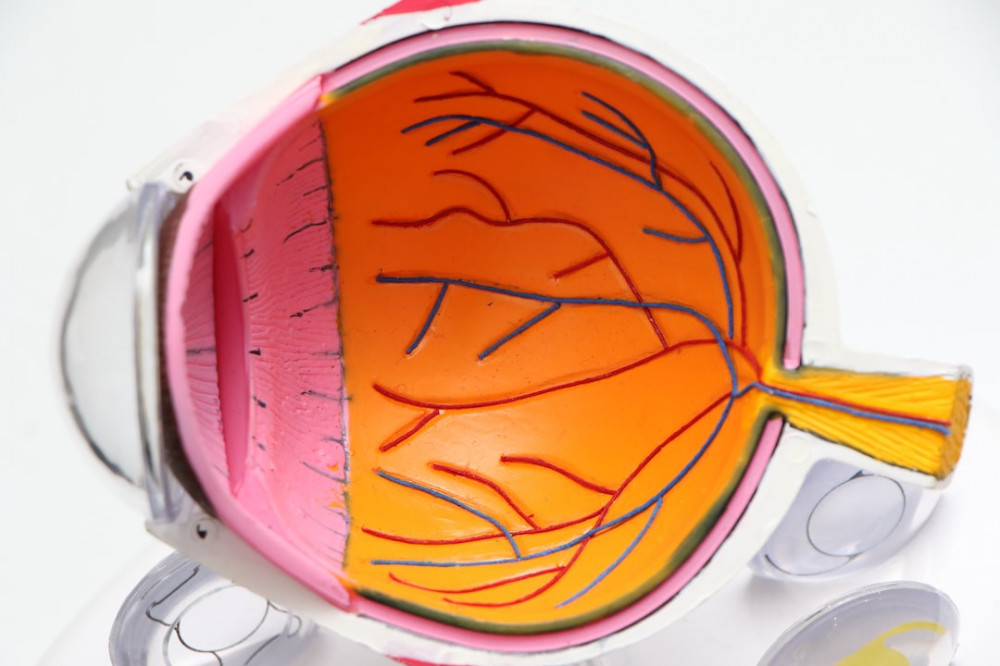
As people age, they become more susceptible to age-related eye conditions that can affect their vision. Some of the most common age-related eye conditions include age-related macular degeneration (AMD), cataracts, glaucoma, dry eye disease, and diabetic retinopathy.
AMD is a leading cause of vision loss in people over the age of 50. It affects the macula, the part of the eye responsible for central vision. There are two types of AMD: dry and wet. Dry AMD is more common and occurs when the macula thins over time, while wet AMD is less common and occurs when abnormal blood vessels grow under the macula. Vitamins and minerals such as vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, and copper have been shown to slow the progression of AMD in some cases, according to the National Eye Institute [1].
Cataracts are another common age-related eye condition that can cause cloudy vision. They occur when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy. While cataracts can be removed with surgery, there is some evidence that vitamins and minerals such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and lutein may help prevent them from forming in the first place [2].
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve and can lead to blindness if left untreated. While there is no cure for glaucoma, early detection and treatment can help slow its progression. Some studies have suggested that vitamins and minerals such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and zinc may help reduce the risk of developing glaucoma [3].
Dry eye disease occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or the tears evaporate too quickly. It is more common in women and in people over the age of 50. While there is no cure for dry eye disease, there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseed oil, may help reduce inflammation in the eyes and improve tear production [4].
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that can cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina. It can lead to vision loss if left untreated. While there is no cure for diabetic retinopathy, controlling blood sugar levels can help slow its progression. Some studies have suggested that vitamins and minerals such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and zinc may help reduce the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy [5].
Overall, while vitamins and minerals may help slow the progression of some age-related eye conditions, it is important to note that they are not a substitute for regular eye exams and proper eye care. Anyone experiencing changes in their vision should consult with an eye care professional.
References
- National Eye Institute. (n.d.). AREDS 2 Supplements for Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD). Retrieved from https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/age-related-macular-degeneration/nutritional-supplements-age-related-macular-degeneration
- Healthline. (2022, February 25). The Top 9 Best Vitamins for Eye Health. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/eye-vitamins
- Healthline. (2022, February 25). The Top 9 Best Vitamins for Eye Health. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/eye-vitamins
- Healthline. (2022, February 25). The Top 9 Best Vitamins for Eye Health. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/eye-vitamins
- Healthline. (2022, February 25). The Top 9 Best Vitamins for Eye Health. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/eye-vitamins
Diet and Eye Health
A healthy diet is essential for maintaining good eye health. Research suggests that foods rich in vitamins C and E, zinc, lutein, zeaxanthin, and omega-3 fatty acids are linked to a lower risk for age-related macular degeneration (AMD), cataracts, and perhaps even dry eye later in life.
To get these important nutrients, experts recommend consuming a diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables, particularly dark green leafy vegetables like spinach, kale, and broccoli. Corn, carrots, pumpkin, sweet potato, and squash are also great sources of eye-healthy nutrients.
Nuts and seeds are also important sources of eye-healthy nutrients. Almonds, walnuts, and sunflower seeds are particularly good choices. Dairy products like milk and cheese can also provide important nutrients for eye health.
Egg yolks are another excellent source of eye-healthy nutrients, particularly lutein and zeaxanthin. Mustard greens and Swiss chard are also rich in these important nutrients.
Avocado is a great source of healthy fats, which are essential for maintaining good eye health. These healthy fats can also be found in foods like salmon and other fatty fish.
In addition to consuming a healthy diet, it is also important to avoid smoking and to protect the eyes from harmful UV rays by wearing sunglasses or a hat with a brim.
Research on Eye Health and Nutrition
There have been numerous studies conducted on the relationship between eye health and nutrition. According to the National Eye Institute, a lack of certain nutrients, including vitamins, carotenoids, and fats, may be one of the reasons why the macula and other parts of the eye may start to deteriorate with age.
The Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS) conducted by the National Eye Institute found that daily supplementation with certain vitamins and minerals reduced the risk of progression to late-stage age-related macular degeneration (AMD) by 25%. The study concluded that a combination of vitamin C (500 mg), vitamin E (400 IU), beta-carotene (15 mg), zinc (80 mg), and copper (2 mg) can help protect against AMD.
The AREDS 2 study expanded on the original study by adding lutein and zeaxanthin to the supplement regimen. These carotenoids were found to be beneficial in reducing the risk of AMD progression in people with low dietary intake of these nutrients.
Other studies have also found that dietary antioxidant vitamins and minerals, such as vitamins A, C, and E, and the mineral zinc, may help prevent the progression of macular degeneration.
In addition to vitamins and minerals, certain nutrients such as anthocyanins, lutein, zeaxanthin, beta-carotene, vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, and selenium have been shown to aid in eye health and reduce the risk of AMD and other eye-related diseases.
Overall, research suggests that a diet rich in these nutrients, either through food or supplements, can help protect and preserve eye health. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Preventing Eye Diseases with a Balanced Diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for maintaining healthy eyesight and preventing eye diseases. Research has shown that certain nutrients can help protect the eyes from age-related macular degeneration (AMD), cataracts, and other eye conditions.
Here are some of the key vitamins and minerals that can help prevent eye diseases:
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is crucial for maintaining good vision, particularly in low light conditions. It is also an antioxidant that helps protect the eyes from damage caused by free radicals. Foods rich in vitamin A include liver, sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach, and kale.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is another powerful antioxidant that can help prevent eye diseases. It helps protect the eyes from damage caused by UV radiation and other environmental factors. Foods rich in vitamin C include oranges, grapefruits, kiwis, strawberries, tomatoes, red and green peppers, and broccoli.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is an antioxidant that can help protect the eyes from damage caused by free radicals. It also helps prevent the development of cataracts and AMD. Foods rich in vitamin E include almonds, sunflower seeds, olive oil, and avocadoes.
Zinc
Zinc is a mineral that is essential for maintaining healthy eyesight. It helps the body absorb vitamin A and also plays a role in the production of melanin, a pigment that protects the eyes from UV radiation. Foods rich in zinc include legumes (beans and lentils), seeds, meat/seafood, dairy, and eggs.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining good eye health. They help prevent dry eye syndrome and also reduce the risk of AMD. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and sardines, as well as flaxseeds and chia seeds.
Incorporating these vitamins and minerals into a healthy, balanced diet can help prevent eye diseases and maintain good eyesight. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet.
Consulting with an Ophthalmologist
When it comes to eye health, consulting with an ophthalmologist is always a good idea. An ophthalmologist is a medical doctor who specializes in eye care and can diagnose and treat eye conditions. They can also provide advice on how to maintain good eye health and prevent future problems.
During a consultation with an ophthalmologist, they will ask about your medical history and any symptoms you may be experiencing. They may also perform a comprehensive eye exam, which can include tests to check your vision, eye pressure, and overall eye health. Based on the results of these tests, they can recommend appropriate treatment options.
If you are concerned about your eye health, or if you are experiencing any symptoms such as blurry vision, eye pain, or redness, it is important to schedule an appointment with an ophthalmologist as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent more serious problems down the road.
In addition to diagnosing and treating eye conditions, ophthalmologists can also provide advice on how to maintain good eye health. This can include recommendations for a healthy diet that includes vitamins and nutrients that are important for eye health, such as vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, and copper. They may also recommend lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, wearing sunglasses to protect your eyes from UV rays, and taking breaks from staring at screens for extended periods of time.
Overall, consulting with an ophthalmologist can provide valuable insight into your eye health and help you maintain good vision for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which vitamins are good for maintaining healthy eyesight?
Vitamins A, C, and E are essential for maintaining good eye health. Vitamin A helps to maintain a clear cornea, which is the outside covering of the eye, and is also a component of rhodopsin, a protein in the retina that allows us to see in low light conditions. Vitamin C helps to reduce the risk of cataracts and macular degeneration, while vitamin E helps to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
What are some foods rich in vitamins that can help improve eyesight?
Foods that are rich in vitamins that can help improve eyesight include leafy greens such as spinach and kale, carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, citrus fruits, berries, nuts, and seeds. These foods are high in vitamins A, C, and E, as well as other nutrients that are essential for maintaining good eye health.
What are the best eye vitamins for improving blurry vision?
While there is no single vitamin that can improve blurry vision, vitamins A, C, and E, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, are important for maintaining good eye health and may help to reduce the risk of developing certain eye conditions that can cause blurry vision.
Can taking eye supplements improve vision?
While taking eye supplements may help to reduce the risk of developing certain eye conditions, such as age-related macular degeneration, they are not a substitute for a healthy diet and lifestyle. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements to ensure that they are safe and appropriate for your individual needs.
Which vitamin is most important for maintaining good eyesight?
While all of the vitamins mentioned above are important for maintaining good eye health, vitamin A is perhaps the most important. In addition to maintaining a clear cornea and playing a crucial role in vision, vitamin A also helps to protect the surface of the eye and may reduce the risk of certain eye infections.
Does vitamin B12 have any impact on eyesight improvement?
While vitamin B12 is important for overall health and may help to reduce the risk of developing certain eye conditions, such as age-related macular degeneration, there is no evidence to suggest that it can improve eyesight in individuals with normal levels of the vitamin.