Welcome to this blog post on the fascinating topic of “Traditional Chinese Medicine vs. Western Medicine.” I understand that when it comes to healthcare, there are various approaches and perspectives that one can consider. That’s I’m here to provide you with valuable insights and information about the differences between these two medical systems. In this post, I will delve into the origins and principles of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and compare it to the well-established practices of Western Medicine. My goal is to help you gain a better understanding of these two approaches, so you can make informed decisions about your own health and well-being. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey together and explore the world of Chinese and Western medicine!
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
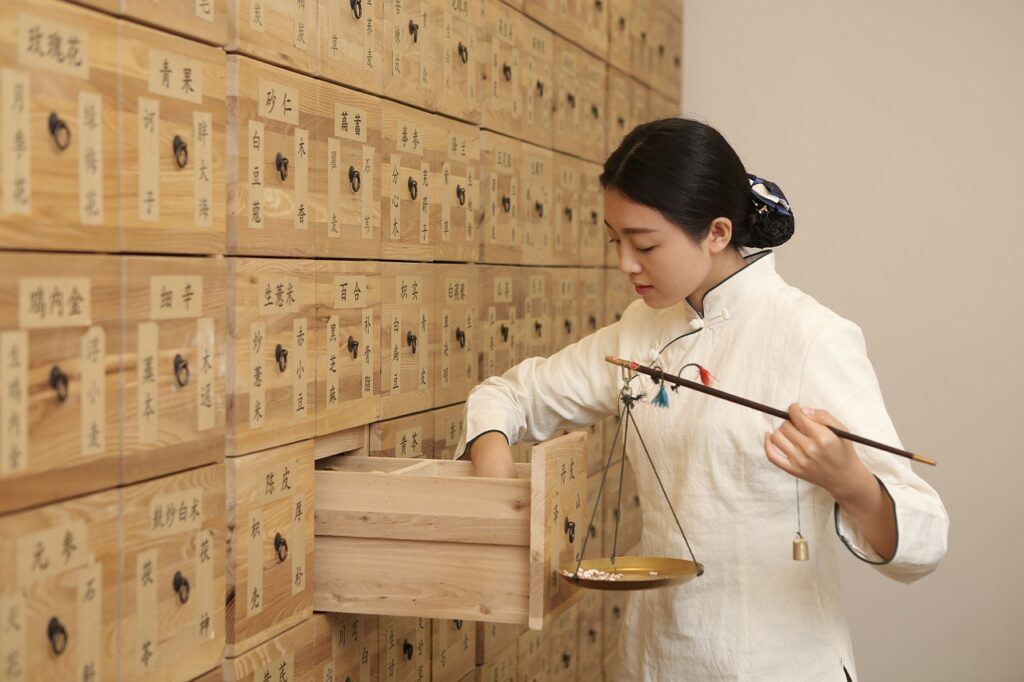
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a comprehensive system of healthcare that has been practiced for thousands of years in China and other parts of East Asia. It is based on a holistic approach to health and wellness, focusing on the balance and harmony of the body, mind, and spirit. In this blog post, we will explore the history, principles, and key modalities of TCM, including acupuncture, herbal medicine, and qigong.
History of TCM
TCM has a rich history that dates back more than 2,500 years. Its origins can be traced to ancient Chinese texts, such as the Huangdi Neijing (Yellow Emperor’s Inner Canon), which laid the foundation for TCM theory and practice. Over the centuries, TCM has evolved and incorporated various influences, including Taoism, Buddhism, and Confucianism. Today, it is recognized as one of the oldest and most comprehensive systems of medicine in the world.
Principles of TCM
At the core of TCM are several key principles that guide its diagnosis and treatment methods. These principles include:
- Yin and Yang: TCM believes that all phenomena can be categorized into Yin (passive, cold, and dark) and Yang (active, warm, and light). Health is achieved when Yin and Yang are in balance, and illness occurs when there is an imbalance between the two.
- Qi: Qi (pronounced “chee”) is the vital energy that flows throughout the body. In TCM, good health depends on the smooth and balanced flow of Qi. When Qi is blocked or depleted, disease and discomfort can arise.
- Five Elements: TCM categorizes the human body and its functions into five elements – Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water. Each element corresponds to specific organs, emotions, and seasons. Imbalances in these elements can lead to various health issues.
Modalities of TCM
TCM encompasses a range of modalities, each with its own unique approach to restoring health and promoting well-being. The three key modalities of TCM are:
1. Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. These points are believed to be connected to channels or meridians through which Qi flows. By stimulating these points, acupuncture aims to restore the balance and flow of Qi, relieving pain and promoting healing. Benefits of acupuncture may include:
- Pain relief: Acupuncture has been found to be effective in managing various types of pain, including chronic pain, migraines, and musculoskeletal disorders.
- Stress reduction: Acupuncture can help reduce stress and promote relaxation, leading to improved overall well-being.
- Improved digestion: Acupuncture can aid in regulating digestion and addressing digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and acid reflux.
2. Herbal Medicine
Is an integral part of TCM and involves the use of natural substances, such as plants, minerals, and animal products, to treat various health conditions. Herbal formulas are carefully prescribed based on individualized diagnoses and aim to restore balance and harmony within the body. Benefits of herbal medicine may include:
- Customized treatment: Herbal medicine offers personalized treatment plans that consider an individual’s unique constitution and symptoms.
- Minimal side effects: When prescribed and used correctly, herbal medicine is generally safe and has fewer side effects compared to synthetic drugs.
- Holistic healing: Herbal medicine addresses not only the symptoms but also the underlying imbalances that contribute to the condition, promoting long-term healing.
3. Qigong
Qigong (pronounced “chee gong”) combines gentle movements, focused breathing, and meditation to cultivate and balance Qi. It is often practiced to promote physical, mental, and spiritual well-being. Benefits of qigong may include:
- Stress reduction: Qigong practices promote relaxation and help reduce stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Improved energy and vitality: Regular practice of qigong can enhance overall energy levels, promote better sleep, and increase vitality.
- Enhanced mind-body connection: Qigong cultivates awareness and mindfulness, promoting a deeper connection between the mind, body, and spirit.
Western Medicine
Western medicine, also known as allopathic medicine, is the dominant system of medical practice in the Western world. It is based on scientific knowledge and evidence-based approaches to diagnose and treat diseases. This blog section aims to provide an informative overview of the principles and practices of Western medicine.
Evidence-based Approaches
Western medicine relies on evidence-based approaches to guide diagnosis and treatment decisions. This means that medical interventions are based on the best available scientific evidence, which is rigorously tested and validated through clinical trials and research studies. The use of evidence-based medicine ensures that treatments have been proven to be effective and safe.
Pharmaceutical Drugs
Pharmaceutical drugs play a crucial role in Western medicine. These drugs are developed through extensive research and testing to target specific diseases and symptoms. They are prescribed based on the individual’s diagnosis and medical history, and their effectiveness is well-documented and supported by scientific evidence.
Benefits of pharmaceutical drugs in Western medicine:
- Targeted treatment for specific diseases or symptoms
- Extensive research and development process ensures safety and efficacy
- Availability of a wide range of medications to address various medical conditions
- Ability to manage chronic diseases and improve quality of life
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions are another important aspect of Western medicine. Surgeons perform various procedures to treat diseases, alleviate symptoms, and improve overall health. Surgical interventions may range from minimally invasive procedures to complex surgeries, depending on the nature of the condition being treated.
Benefits of surgical interventions in Western medicine:
- Ability to treat conditions that cannot be managed through medication alone
- Immediate and sometimes life-saving interventions
- Improved outcomes for a wide range of medical conditions
Reductionist Approach
Western medicine is often criticized for its reductionist approach, which focuses on treating specific symptoms or diseases rather than considering the whole person. This approach is rooted in the idea that diseases can be understood and treated by breaking them down into smaller components.
Key points regarding the reductionist approach in Western medicine:
- Emphasis on identifying specific causes and developing targeted treatments
- Focus on disease management rather than holistic well-being
- Limited attention to underlying lifestyle factors or psychological aspects of health
Comparison of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and Western medicine are two distinct approaches to healthcare that have evolved over centuries in different cultural contexts. While Western medicine is widely practiced and accepted in many parts of the world, TCM continues to be a popular and effective alternative in various regions. Understanding the key differences between these two systems can help individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare options. In this blog post, we will compare and contrast TCM and Western medicine across various factors, including underlying philosophies, diagnostic methods, treatment approaches, emphasis on prevention, cultural context, and patient-doctor relationship.
Underlying Philosophies
- TCM: Based on the concept of balance and harmony between yin and yang energies, as well as the flow of Qi (vital energy). The focus is on maintaining the body’s overall equilibrium to promote health and prevent diseases.
- Western medicine: Grounded in the scientific method and evidence-based practices. It emphasizes the understanding of diseases through anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry, aiming to diagnose and treat specific medical conditions.
Diagnostic Methods
- TCM: Diagnostic methods include observing the patient’s appearance, tongue, and pulse, as well as asking detailed questions about symptoms and medical history. It also considers emotional and environmental factors.
- Western medicine: Diagnostic methods rely on physical examinations, laboratory tests, imaging techniques, and medical history interviews to identify specific diseases or conditions.
Treatment Approaches
- TCM: Treatment involves the use of various therapies, including acupuncture, herbal medicine, massage (Tui Na), dietary therapy, and mind-body exercises (such as Tai Chi and Qigong). It aims to restore balance and improve overall health.
- Western medicine: Treatment typically involves pharmaceutical drugs, surgical interventions, and other evidence-based procedures targeted at specific diseases or conditions.
Emphasis on Prevention
- TCM: Places a strong emphasis on preventive measures such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, stress reduction, and regular exercise to prevent diseases before they occur.
- Western medicine: While prevention is recognized as important, Western medicine often focuses more on the diagnosis and treatment of diseases rather than proactive measures.
Cultural Context
- TCM: Rooted in Chinese culture and philosophy, TCM incorporates holistic principles and considers the interplay between the body, mind, and environment. It is deeply integrated into everyday life and has been practiced for thousands of years.
- Western medicine: Developed in Western societies and influenced by scientific advancements, Western medicine is widely accepted and practiced in many parts of the world. It places a strong emphasis on evidence-based practices and clinical research.
Patient-Doctor Relationship
- TCM: The patient and doctor have a more collaborative and holistic relationship. The doctor considers the patient’s entire well-being and aims to educate and empower the individual to take an active role in their own healthcare.
- Western medicine: The patient-doctor relationship is often more authoritative, with the doctor having the primary decision-making role. The focus is on diagnosing and treating specific medical conditions.
Strengths and Limitations
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
- Strengths:
- Holistic approach to healthcare, addressing the mind, body, and spirit.
- Emphasis on prevention and maintaining overall well-being.
- Wide range of non-invasive treatment options.
- Individualized treatment plans based on the patient’s unique constitution.
- Limitations:
- Lack of standardized scientific evidence for some practices.
- Limited integration with modern medical technologies.
- Language and cultural barriers may pose challenges in understanding and acceptance.
Western Medicine
- Strengths:
- Scientifically rigorous and evidence-based approach.
- Highly advanced diagnostic and treatment technologies.
- Well-integrated with modern healthcare systems.
- Strong emphasis on specialized care for specific diseases.
- Limitations:
- Focuses more on symptom management rather than holistic well-being.
- Potential side effects of pharmaceutical drugs and invasive procedures.
- Limited emphasis on preventive measures.
In conclusion, TCM and Western medicine have distinct approaches to healthcare, reflecting their underlying philosophies and cultural contexts. While TCM emphasizes holistic well-being and prevention, Western medicine focuses more on specific disease diagnosis and treatment. Both systems have their strengths and limitations, and individuals may choose to integrate elements of both approaches depending on their healthcare needs and preferences.
Integration and Collaboration
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the integration and collaboration between Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and Western medicine. This exciting development recognizes the unique strengths of both systems and aims to provide a more comprehensive approach to healthcare. By combining the ancient wisdom of TCM with the scientific advancements of Western medicine, we have the potential to unlock new possibilities in patient care and treatment.
Complementary Approaches for Enhanced Healthcare
Holistic View vs. Reductionist Approach
One of the key differences between TCM and Western medicine lies in their underlying philosophies. TCM takes a holistic view of health, focusing on the balance and harmony of the body, mind, and spirit. On the other hand, Western medicine often adopts a reductionist approach, breaking down health issues into specific symptoms and treating them accordingly.
Yin-Yang and Qi vs. Anatomy and Physiology
TCM recognizes the concept of Yin-Yang and Qi (vital energy) as fundamental elements for maintaining health. Western medicine, on the other hand, places emphasis on anatomy, physiology, and biochemical processes. Both systems, however, share the goal of restoring and maintaining optimal health.
Integration: The Best of Both Worlds
By integrating the strengths of TCM and Western medicine, we can achieve a more comprehensive and personalized approach to patient care. Here are some examples of how these two systems can complement each other:
- Holistic Diagnosis: TCM diagnosis methods, such as pulse and tongue examination, can provide valuable insights into a patient’s overall health and help identify underlying imbalances. This information can be used alongside Western diagnostic tools, such as blood tests and imaging techniques, to create a more complete picture of the patient’s health status.
- Combination Therapies: Integrative treatment plans may include a combination of TCM therapies, such as acupuncture, herbal medicine, and dietary changes, alongside Western medical interventions like medications and surgeries. This approach can enhance the effectiveness of treatment and minimize side effects.
- Preventive Care: TCM’s emphasis on preventive care and maintaining balance can complement Western medicine’s focus on acute and chronic disease management. By integrating TCM practices into routine healthcare, we can potentially prevent the onset of certain conditions and promote overall well-being.
The Rise of Integrative Medicine
The interest in integrating TCM and Western medicine is not limited to patients and practitioners. Even healthcare institutions and academic researchers are recognizing the potential benefits of this collaborative approach. The field of integrative medicine is rapidly expanding, with dedicated centers and programs being established worldwide.
Evidence-Based Research: Validating TCM Practices
To ensure the safety and effectiveness of TCM practices, it is crucial to conduct rigorous scientific research. Evidence-based research plays a vital role in validating TCM modalities and providing a solid foundation for integration. Recent studies have shown promising results in areas such as acupuncture for pain management, herbal medicine for certain conditions, and mind-body practices for stress reduction.
Comparing the benefits and limitations of two different approaches to healthcare
In conclusion, we have explored the differences between Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and Western medicine. We have discussed how TCM focuses on holistic healing, balancing the body’s energy, and using natural remedies, while Western medicine relies on scientific evidence, pharmaceuticals, and advanced technology.
Considering these factors, we recommend taking an individualized approach to healthcare. By combining the strengths of both TCM and Western medicine, patients can benefit from a comprehensive and balanced approach to their well-being.
It is important to consult with qualified healthcare professionals who can guide us in making informed decisions about our health. They can help us navigate the complexities of both TCM and Western medicine, and tailor treatment plans to our specific needs.
Ultimately, the goal is to achieve optimal health and wellness. By embracing a collaborative and open-minded approach, we can harness the diverse benefits of both TCM and Western medicine, ensuring that we receive the best possible care for our individual needs.